
The history of animation started in the early 19th century and has been inextricably linked with the development of still photography. Early animations were made from a series of still images shown in sequential order, most commonly the 24 frame_per second of projected film. which were still images which appear to move because of a phenomenon known as persistence of vision, in which the eye refrains the projected image for a fraction of a second before it is replaced by the next one. the brain is then tricked into seeing the rapid sequences in the way most familiar to it.

The earliest example of moving pictures started to appear in the 19th century,which was created from a belgian physicist joseph plateau who created the device called the Phenkakistiscope, this was a disk with a sequence of eight drawings that were viewed through slots and reflected in the mirror. The phenkakistiscope was made in 1832 also during the the 19 century.
Example of a Phenkakistiscope

Example of a Zoetrape
The Praxinoscope was invented by french scientist Charles-Emile Reynaud , it combines the cylindrical design of the Zoetrope with the viewing mirror of the Phenakistoscope. the mirrors are mounted still in the centre of the spinning ring of slots and drawings so that the image can be more clearly seen no matter what the device's radius are.

The Praxinoscope was invented by french scientist Charles-Emile Reynaud , it combines the cylindrical design of the Zoetrope with the viewing mirror of the Phenakistoscope. the mirrors are mounted still in the centre of the spinning ring of slots and drawings so that the image can be more clearly seen no matter what the device's radius are.

Example of a Praxinoscope
The Kinetoscope was made in 1984, which was an early motion picture exhibition device. the Kinetoscope was designed for films to be viewed by one person at a time through a peephole viewer window at the top of he device, its creates illusions of movements by passing on a strip of perforated film bearing sequential images over the light source with a high-speed shutter.

The Kinetoscope was made in 1984, which was an early motion picture exhibition device. the Kinetoscope was designed for films to be viewed by one person at a time through a peephole viewer window at the top of he device, its creates illusions of movements by passing on a strip of perforated film bearing sequential images over the light source with a high-speed shutter.

Example of a Kinetoscope
Example of a mutoscope
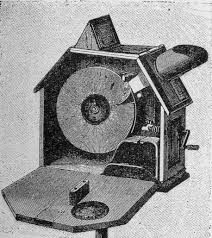
Vitascope


Phi Phenomenon

beta movement

The beta movement is a optical that is fixed images seem to move, even though of course the image does not change. it might be considered similar to the effects of animation.
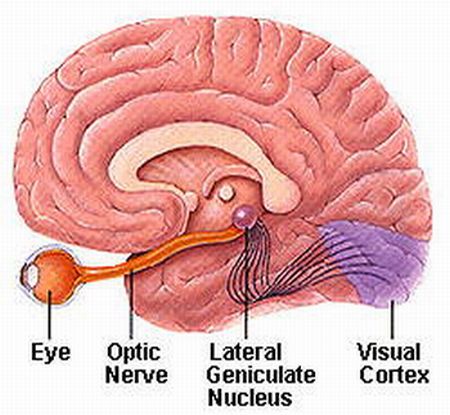
Optic nerve registers light at 10 cycles per second
Persistence of vision - physical eye function
Persistence of motion - mental brain function
Silent Era


Example of both fantasmagorie on the left and humpty dumpty circus on the right

lumiere brothers
Charles-Emile Reynaud's Theatre Optique is the earliest known example of projected animation. It predates even photographic video devices such as Thomas Edison's 1883 invention, the Kinetoscope, and the 'Lumiere brothers' 1884 invention, the cinematograph. Reynaud exhibited three of his animations on October 28, 1892 at Musée Grévin in Paris, France. The only surviving example of these three is Pauvre Pierrot which was 500 frames long.
After the cinematograph popularized the motion picture, the endless possibilities of animation began to be explored in much greater depth. A short stop-motion animation was produced in 1908 by Albert E. Smith and J. Stuart Blackton called The Humpty Dumpty Circus.Stop motion is a video technique in which real objects are moved around in the time between their images being recorded so that when the images are viewed as a video, they appear to be moving by some invisible force.
Fantasmagorie, by the French director Emile Courtet, is also noteworthy. It was screened for the first time on August 17, 1908 at Théâtre du Gymnase in Paris. Cohl later went to Fort Lee,New Jersey near New York City in 1912, where he worked for French studio Éclair and spread its animation technique to the US.
The Golden Age of Animation

In 1923 a studio
called Laugh-O-Grams went bankrupt and its owner Walt Disney opened a
new studio in Los Angeles
The Television Era



Terrytoons, Tom terrific and the Flintstones
What i liked about these eras, is that it was very similar to stop motion animation and filming, in terms of how music,picture,sound were all linked together from old to new age. They were created drawing on layered see through paper , in modern days some people yous animation software's, like flash, anime studio etc.

No comments:
Post a Comment